PracticeSuite for Dermatology
Manage your entire practice on a single cloud-based system meant for sustaining and scaling your practice’s success. PracticeSuite’s full suite of practice management solutions is designed to meet the needs of busy dermatologists.
Support Practice Growth with PracticeSuite
Proven Revenue Cycle Management solutions that can identify and fix lost revenue from patient balances and unpaid claims.
or call
(813) 607-2255
We never share your information with anyone
Practice Management modules built to fit the way that you run your practice.
Communicate with patients in ways most convenient to them
Keep everything seamlessly connected to ensure top performance for your practice
Software that quickly leads providers through procedure codes

Extra support for your front-office staff to keep things running smoothly
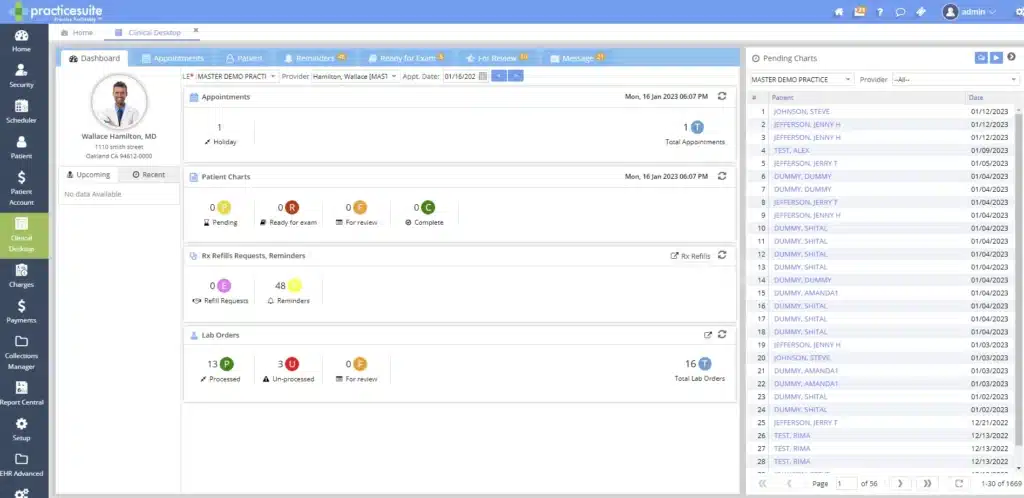
Adaptable dashboards and workflows that truly work
Simplify image comparison and gather data from different imaging devices


